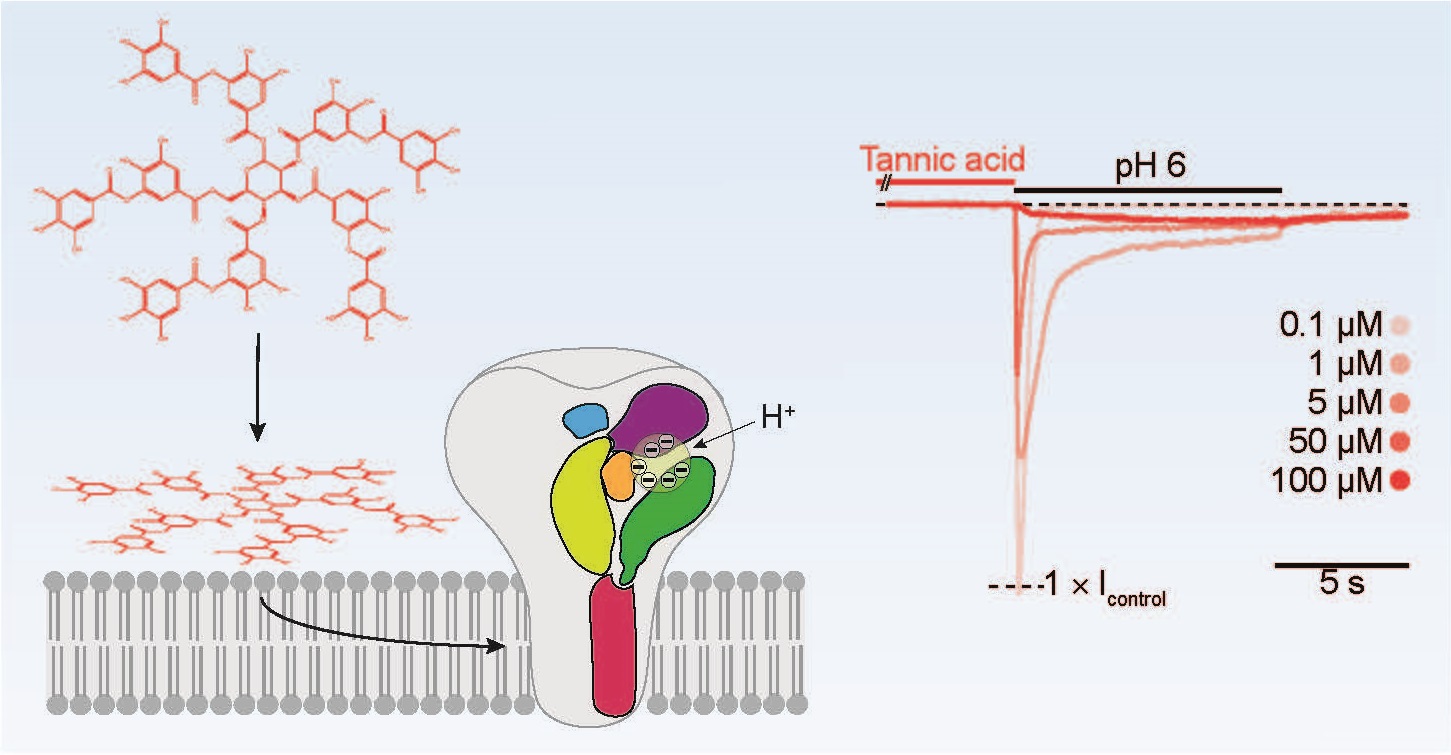
Phytochemicals represent a large pool of substances with the potential to modulate diverse proteins, for example ion channels. In our recent study, which has been published in the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00032), we found that acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are modulated by tannic acid and green tea. In addition, we could show that the mechanism of this modulation is most likely an alteration of the properties of the plasma membrane. Because tannic acid and green tea modulate also other ion channels, it is likely that alteration of the membrane properties is the common mechanism of these modulations.
Für Presserückfragen wenden Sie sich bitte an:
Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
Stabsstelle Unternehmenskommunikation
Dr. Mathias Brandstädter
Tel. 0241 80-89893
kommunikationukaachende