Juliane Bremer

Jun.-Prof. Dr. med. Dr. sc. nat. Juliane Bremer
Attending physician and group leader
Tel.: 0241 80-89418
jbremerukaachende
Research aims
We use zebrafish to model neuromuscular diseases. Using zebrafish allows us to combine genetic tools (CRISPR/Cas9, transgenesis), modern imaging tools, histological and ultrastructural analysis as well as compound library screens to determine the pathophysiology of neuromuscular diseases like Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, hereditary peripheral neuropathies and muscle diseases. We focus on determining whether genes that are mutated in neuromuscular diseases control development, maintenance and regeneration of nerves and skeletal muscle. Findings in zebrafish are correlated with clinicopathological observations in affected patients.
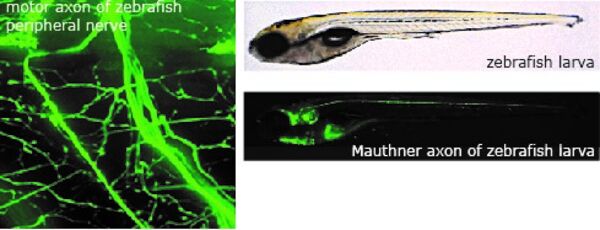
Zebrafish, CRISPR/Cas9, neuromuscular diseases, spinning disc confocal microscope, compound library screen
Yan Feng
Medical doctoral student
Martin Groß, BSc, MSc
PhD student
Tayfun Palaz, BTA
Technician
Elisabeth Helene Stiegelmeier
Bachelor student
Xiaomeng Zhang
Medical doctoral student
2022: DFG funding for a spinning disk confocal microscope with ablation and FRAP laser
Postdoctoral training:
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA, supervisor: Prof. Michael Granato
PhD training:
Institute of Neuropathology, University Hospital Zürich, Switzerland, supervisor: Prof. Adriano Aguzzi
Medical training:
Institute of Neuropathology, Pathology and Department of Neurology of the University Hospital Zürich, Switzerland
Jütten K, Ort J, Kernbach JM, Meyer-Baese A, Meyer-Baese U, Hamou HA, Clusmann H, Wiesmann M, Bremer J, Koch H, Bak A, Ricklefs F, Drexler R, Heiland DH, Delev D. High peritumoral network connectedness in glioblastoma reveals a distinct epigenetic signature and is associated with decreased overall survival. Neuro Oncol. 2025 Apr 15:noaf101. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaf101. Online ahead of print.PMID: 40230019
Bremer J, Franco P, Menstell JA, Tey S, Zajt KK, Popzhelyazkova K, Nolte K, Schlegel J, Pedro M T, Osterloh A, Delev D, Hohenhaus M, Scholz C, Schnell O, Beck J, Weis J, Heiland DH. Spatially resolved transcriptomics of benign and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2025 Jan 23:noaf016. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaf016. PMID: 39847441
Kraft F, Rodriguez-Aliaga P, Yuan W, Franken L, Zajt K, Hasan D, Lee TT, Flex E, Hentschel A, Innes AM, Zheng B, Julia Suh DS, Knopp C, Lausberg E, Krause J, Zhang X, Trapane P, Carroll R, McClatchey M, Fry AE, Wang L, Giesselmann S, Hoang H, Baldridge D, Silverman GA, Radio FC, Bertini E, Ciolfi A, Blood KA, de Sainte Agathe JM, Charles P, Bergant G, Čuturilo G, Peterlin B, Diderich K, Streff H, Robak L, Oegema R, van Binsbergen E, Herriges J, Saunders CJ, Maier A, Wolking S, Weber Y, Lochmüller H, Meyer S, Aleman A, Polavarapu K, Nicolas G, Goldenberg A, Guyant L, Pope K, Hehmeyer KN, Monaghan KG, Quade A, Smol T, Caumes R, Duerinckx S, Depondt C, Van Paesschen W, Rieubland C, Poloni C, Guipponi M, Arcioni S, Meuwissen M, Jansen AC, Rosenblum J, Haack TB, Bertrand M, Gerstner L, Magg J, Riess O, Schulz JB, Wagner N, Wiesmann M, Weis J, Eggermann T, Begemann M, Roos A, Häusler M, Schedl T, Tartaglia M, Bremer J, Pak SC, Frydman J, Elbracht M, Kurth I: Brain malformations and seizures by impaired chaperonin function of TRiC. Science. 2024 Nov; 386(6721):516-525.doi:10.1126/science.adp8721. PMID: 39480921
Haag N, Bremer J, Zempel H: Understanding genetics, sex and signaling: Implications of sex-dependent APOE4-neutrophil-microglia interactions for Alzheimer´s and tauopathies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 23;9(1):252. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01967-1.PMID:39313493
Caredio D, Koderman M, Frontzek KJ, Sorce S, Nuvolone M, Bremer J, Mariutti G, Schwarz P, Madrigal L, Mitrovic M, Sellitto S, Streichenberger N, Scheckel C, Aguzzi A (2024): Prion diseases disrupt glutamate/glutamine metabolism in skeletal muscle. PLoS Pathog. 20 (9): e1012552. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012552. PMID: 39259763
Grübel N, Antoniadis G, Uerschels AK, Gembruch O, Marschal V, Deininger S, König R, Pala A, Bremer J, Dengler NF, Reuter M, Wirtz CR, Pedro MT (2024) : Collection of Rare Peripheral Nerve Tumors-Insights from the German Registry. Cancers (Basel). 16 (14): 2599. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142599. PMID: 39061237.
Grübel N, Antoniadis G, König R, Wirtz CR, Bremer J, Pala A, Reuter M, Pedro MT. Case report: Atypical neurofibromatous neoplasm with uncertain biological potential of the sciatic nerve and a widespread arteriovenous fistula mimicking a malignant peripheral nerve tumor in a young patient with neurofibromatosis type 1. Front Oncol. 2024 May10; 14; 1391456. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1391456. eCollection 2024.PMID: 38800392
Bremer J, Meinhardt A, Katona I, Senderek J, Kämmerer-Gassler EK, Roos A, Ferbert A, Schröder JM, Nikolin S, Nolte K, Sellhaus B, Popzhelyazkova K, Tacke F, Schara-Schmidt U, Neuen-Jacob E, de Groote CC, de Jonghe P, Timmerman V, Baets J, Weis J. Myelin protein zero mutation-related hereditary neuropathies: Neuropathological insight from a new nerve biopsy cohort. Brain Pathol. 2023 Aug 15:e13200. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13200. Online ahead of print. PMID: 37581289
Bremer J, Friemann J, von Stillfried S, Boor P, Weis J (2023): Reduced T-cell densities in cranial nerves of patients who died with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Acta Neuropathologica Communcations; 11 (1): 10
O'Connor T, Zhou X, Kosla J, Adili A, Garcia Beccaria M, Kotsiliti E, Pfister D, Johlke AL, Sinha A, Sankowski R, Schick M, Lewis R, Dokalis N, Seubert B, Höchst B, Inverso D, Heide D, Zhang W, Weihrich P, Manske K, Wohlleber D, Anton M, Hoellein A, Seleznik G, Bremer J, Bleul S, Augustin HG, Scherer F, Koedel U, Weber A, Protzer U, Förster R, Wirth T, Aguzzi A, Meissner F, Prinz M, Baumann B, Höpken UE, Knolle PA, von Baumgarten L, Keller U, Heikenwalder M. (2019): Age-Related Gliosis Promotes Central Nervous System Lymphoma through CCL19-Mediated Tumor Cell Retention. Cancer Cell. 36 (3): 250-267.
Bremer J, Marsden KC, Miller A, Granato M. (2019): The ubiquitin ligase PHR promotes directional regrowth of spinal zebrafish axons. Commun Biol. 2: 195
Ducommun Priest M, Navarro MF, Bremer J, Granato M (2019): Dynein promotes sustained axonal growth and Schwann cell remodeling early during peripheral nerve regeneration. PLoS Genet. 15(2): e1007982
Bremer J, Skinner J, Granato M (2017): A small molecule screen identifies in vivo modulators of peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish. PLoS One. 12 (6): e0178854.
Bremer J, Granato M (2016): Myosin phosphatase fine-tunes zebrafish motoneuron position during axonogenesis. PLoS Genetics. 12 (11): e1006440.
Bremer J, O’Connor T, Tiberi C, Rehrauer H, Weis J, Aguzzi A (2010): Ablation of Dicer from murine Schwann cells increases their proliferation while blocking myelination. PLoS One. 5 (8): e12450.
Bremer J, Baumann F, Tiberi C, Wessig C, Fischer H, Schwarz P, Steele AD, Toyka KV, Nave KA, Weis J, Aguzzi A (2010): Axonal prion protein is required for peripheral myelin maintenance. Nature Neurosci. 13 (3): 310-318.
Bremer J, Heikenwalder M, Haybaeck J, Tiberi C, Krautler NJ, Kurrer MO, Aguzzi A (2009): Repetitive immunization enhances the susceptibility of mice to peripherally administered prions. PLoS One. 4 (9): e7160.
Haybaeck J, Zeller N, Wolf MJ, Weber A, Wagner U, Kurrer MO, Bremer J, Iezzi G, Graf R, Clavien PA, Thimme R, Blum H, Nedospasov SA, Zatloukal K, Ramzan M, Ciesek S, Pietschmann T, Marche PN, Karin M, Kopf M, Browning JL, Aguzzi A, Heikenwalder M (2009): A lymphotoxin-driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 16 (4): 295-308.
Aguzzi A, Baumann F, Bremer J (2008): The prion's elusive reason for being. Annu Rev Neurosci. 31: 439-77. Review.
