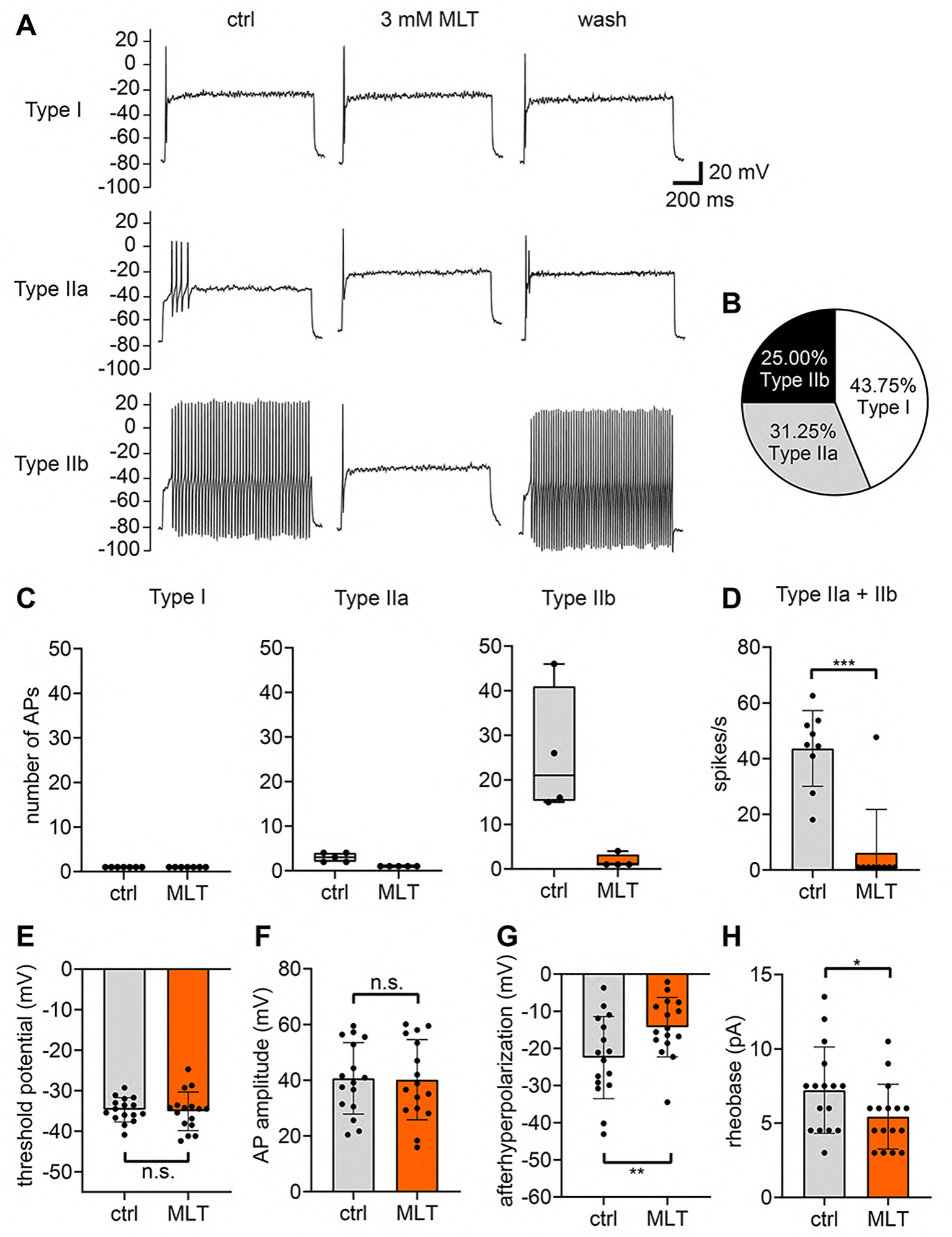
Melatonin is well known as “sleeping hormone”. In the USA and Canada, it is also sold as an over-the-counter dietary supplement and strong antioxidative effects and positive effects on diverse diseases, including cancer, have been attributed to melatonin. However, these beneficial effects often require unphysiologically high (millimolar) concentrations of melatonin. In our recent study, which has been published in the Journal of Pineal Research (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jpi.12919), we found that high concentrations of melatonin strongly reduce the excitability of cerebellar granule cells, one of the most numerous neurons in the brain. Moreover, we found that melatonin inhibits different types of voltage-gated ion channels, most likely via an unspecific mechanism. These profound effects of melatonin on neurons are a potentially important side effect, which should be considered when administering high concentrations of melatonin.
Für Presserückfragen wenden Sie sich bitte an:
Uniklinik RWTH Aachen
Stabsstelle Unternehmenskommunikation
Dr. Mathias Brandstädter
Tel. 0241 80-89893
kommunikationukaachende

![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/9/6/csm__ME18759_4dcd3c7cfd.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/4/6/csm__ME18836_e9746e1c31.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/d/e/csm__ME18866_8e2719aa71.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/b/6/csm__ME18941_58dbfb528e.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/0/7/csm__ME18965h_2b5a133f2a.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/a/5/csm__ME18992_688dd41c10.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/1/1/csm__ME19185_8a61b218cf.jpg)
![[Translate to en:] [Translate to en:]](/fileadmin/files/institute/physiologie/_processed_/7/5/csm__ME27611_14f178eb7a.jpg)